Site and Site Configuration
Site
A site in our EMS system represents an entity such as a factory, business office, or apartment building. Typically, a site is defined by a single connection to the electrical grid. Each site operates as an independent entity, managing energy flow, monitoring devices, and optimizing operations for its designated grid connection.
Site Configuration
The site configuration defines the topology of the site that requires optimization. Without a proper configuration, the system cannot generate accurate optimization recommendations.
This section provides an overview of the key components of a typical site configuration, which consists of two main elements: the collector list and the device list.
Collector List
The collector list defines the relevant collectors within the electrical grid being optimized. Future updates will support multiple collectors with different commodities (e.g., electricity, gas, hot water), but currently, only electricity collectors are supported.
Collectors are organized in a parent-child hierarchy, where different attributes may be required depending on their role.
Parent (Main) Collector
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | Unique identifier for the collector (all characters except spaces are accepted). Example: ALSB |
commodity | Currently, this must be set to electricity. |
line_current | Maximum line_current that passing through this collector in amperes |
line_voltage | (deprecated: use phase_voltage) Maximum line voltage (in volts) passing through this collector. |
phase_voltage | Maximum phase voltage (in volts) passing through this collector. |
1P_3P | Specifies whether the collector is single-phase ("1P") or three-phase ("3P"). |
children | A list of sub-collectors linked to this collector. _commodity_ and _line_voltage_ are not required here. |
Example Payload
{
"name": "MainCollector",
"commodity": "electricity",
"line_current": 1000,
"phase_voltage": 230,
"1P_3P": "3P",
"children": [
{
"name": "SubCollector1",
"line_current": 500,
"1P_3P": "3P"
}
]
}
Child (Sub) Collector
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | Unique identifier for the collector (all characters except spaces are accepted). Example: ALSB_PV. |
commodity | Currently, this must be set to electricity. |
line_current | Maximum line current (in amperes) for this collector. |
1P_3P | Specifies whether the collector is single-phase ("1P") or three-phase ("3P"). |
line_voltage | (deprecated: use phase_voltage) Maximum line voltage (in volts) passing through this collector. |
phase_voltage | (Optional) Maximum phase voltage (in volts) passing through this collector. |
children | (Optional) A list of sub-collectors linked to this collector. _commodity_ and _line_voltage_ are not required for child collectors. |
phase | (Optional) If a single-phase child collector is linked to a three-phase parent, specify the phase ("L1", "L2", or "L3"). |
phase_permutations | (Optional) If the phase naming conventions (L1, L2, L3) are not consistent between parent and child, specify the phase mapping between them. |
Setting a different line voltage in a child collector allows the inclusion of transformers, but transformer losses are not accounted for.
Example Payload
{
"name": "SubCollector1",
"commodity": "electricity",
"line_current": 500,
"1P_3P": "3P",
"phase_voltage": 230,
"children": [],
"phase": "L1",
"phase_permutations": {
"parent_phase": "L1",
"child_phase": "L2"
}
}
Device List
3-Phase Charging Station
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | Unique identifier (all characters except spaces are accepted). Names should differ from collector names. |
type | Must be set to "charging_pole_3phase". |
line_current | Maximum line current (in amperes). |
collector | Name of the collector to which the charging pole is connected. Must be a three-phase electricity collector. |
pin_to_phase_mapping | Defines how charging pole pins map to the collector’s phases. |
Example Payload
{
"name": "ChargingStation3P",
"type": "charging_pole_3phase",
"line_current": 32.0,
"collector": "MainCollector",
"pin_to_phase_mapping": {
"pin_list": ["pin1", "pin2", "pin3"],
"phase_list": ["L1", "L2", "L3"]
}
}
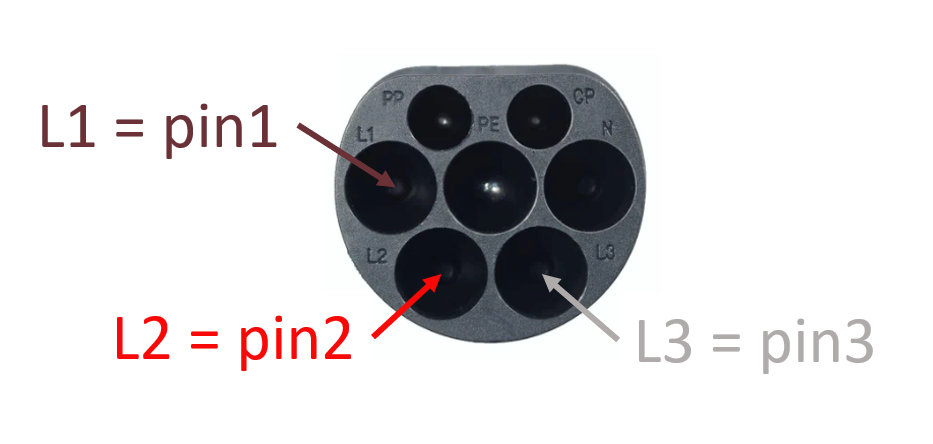
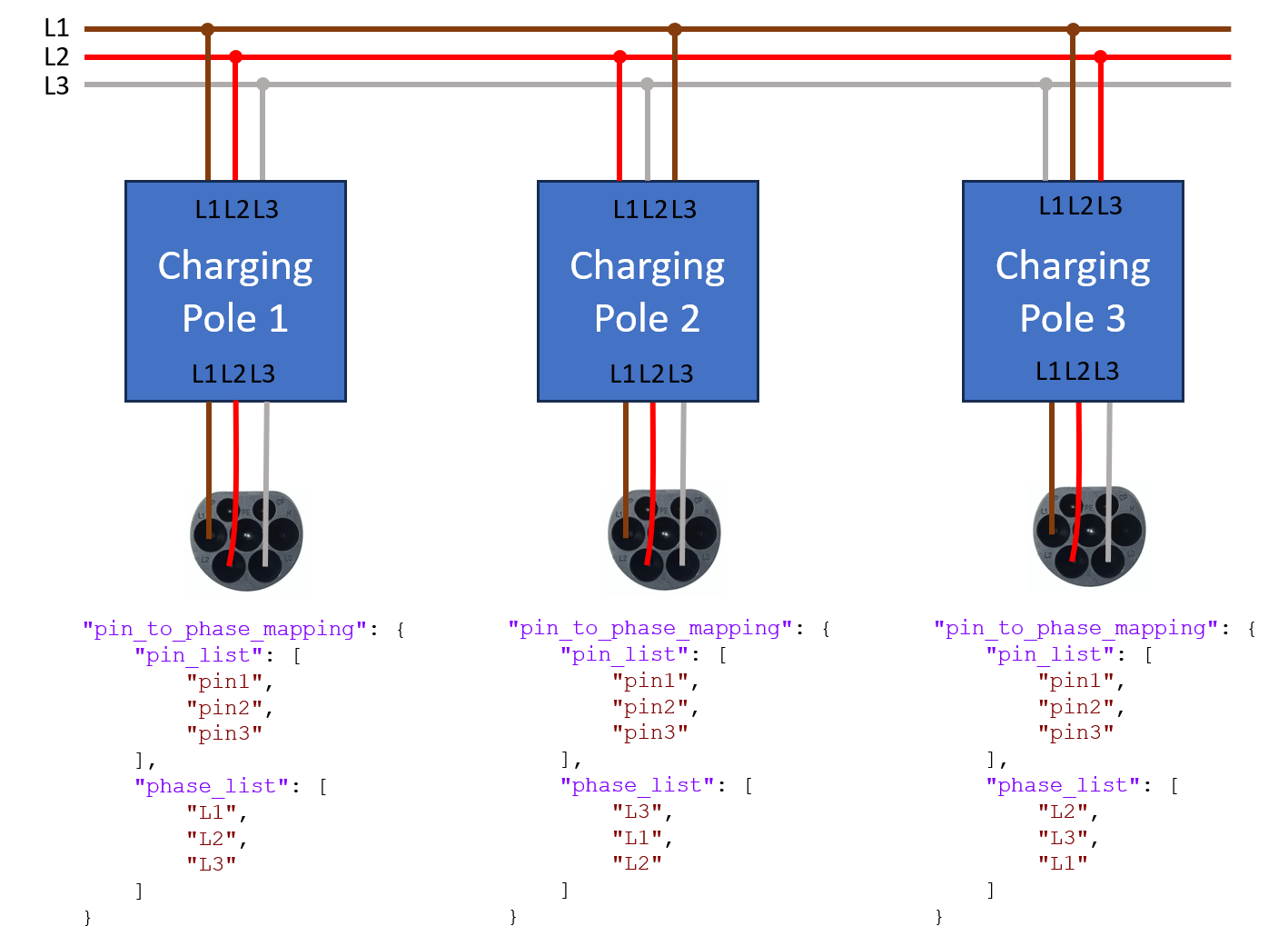
In order to balance power over the phases when lots of single phase charging sessions are ongoing, it is common practice to rotate the phases of the charging stations. In order to make sure that the optimization software calculates the power on each phase correctly, it is important that phase mapping of each individual charging pole is correctly configured. The figure below shows the pinning of a CCS type 2 connector, having 3 pins connecting the phases of the grid to the car. On the connector they are referred to as L1, L2 and L3 but that does not mean that they are actually connected to the L1, L2 and L3 phases of the grid. In the terminology below, pins refer to the pins of the connector.

The figure below shows how rotating phases should be configured in the pin_to_phase_mapping field of a three-phase charging pole. The pin_list refers to the physical pins on the connector, the phase_list refers to the phases of the grid.
1-Phase Charging Station
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
type | Must be set to "charging_pole_1phase". |
name | Unique identifier. Cannot be reused in collector specifications. |
line_current | Maximum line current (in amperes). |
collector | Name of the collector to which the device is connected. |
phase | (Mandatory if connected to a three-phase collector) Specifies the phase ("L1", "L2", "L3"). |
The charging pole inherits the voltage from the collector it is connected to.
Example Payload
{
"type": "charging_pole_1phase",
"name": "ChargingStation1P",
"line_current": 16.0,
"collector": "SubCollector1",
"phase": "L2"
}
3-Phase Forecasted Series
A forecasted series can be added for any non-controllable three-phase device with predictable energy patterns.
Currently, we support photovoltaic (PV) (and soon uncontrollable load (UCL)) forecasting.
Example Payload
{
"type": "forecasted_series_3phase",
"name": "ForecastSeries3P",
"collector": "MainCollector",
"line_current": XXXX,
"type": "pv" or "load"
}
This document provides a structured guide to configuring sites within the EMS system, ensuring accurate energy optimization for different setups.